Global branding is defined as the strategy of creating and maintaining a consistent brand identity across all different countries and their cultures. This marketing practice includes creating a unified brand image and message that has the potential to resonate and connect with diverse audiences all over the globe.
Some Effective Global Branding Approaches
When venturing into global branding, it’s crucial to adopt a strategic mindset.
Utilize proven global branding strategies to steer your international ventures and enrich your global brand presence. Here are some effective approaches.
Establish clear goals
Define measurable objectives that harmonize with your overarching business strategy, providing benchmarks for evaluating international performance.
Analyze global competitors
Gain insights into competitors’ strengths and weaknesses to pinpoint opportunities and tailor your tactics accordingly.
Embrace social responsibility
Incorporate ethical and sustainable practices into your approach, appealing to socially conscious consumers and bolstering credibility on a worldwide scale.
Cultivate internal global communication
Ensure teams across diverse regions are aligned with the brand’s vision, values, and messaging.
A cohesive internal communication strategy promotes consistency.
Evaluate global product positioning
Scrutinize how products or services are positioned in different markets. Adapt offerings, pricing strategies, and content marketing to resonate with local preferences.
What is International Branding?
International branding involves establishing and promoting a consistent image and identity for a product, service, or company across multiple countries and cultures. It is achieved through meticulous market research, strategic planning, and targeted communication efforts.
Companies must adapt their branding strategies to suit diverse cultural norms, consumer preferences, and market conditions in each target country. This typically involves tailoring messaging, packaging, pricing, and promotional activities to resonate with local audiences while still maintaining core brand values and positioning.
Effective international branding requires careful coordination across all aspects of the business to ensure a unified and impactful presence in global markets.
Effective International Branding Strategies for Businesses

In the ever-connected world of today, international branding has become accessible and affordable for businesses of all sizes and industries. The Internet and online marketing have opened up avenues for reaching emerging overseas markets that were previously unimaginable. However, simply being online isn’t enough to build a global brand with staying power; it requires strategic planning and execution.
Website Marketing
Your website serves as your digital storefront, making it essential for international branding. Ensure your website is optimized for different markets by focusing on high-quality content translation, local SEO, and domain structure consistency.
Culture Sensitivity
Cultural norms and differences play a significant role in branding. Understanding and respecting cultural nuances, such as language preferences and communication styles, can help build strong connections with international customers.
Adapt to Buying Preferences
Purchasing behaviors vary across countries. Tailor your purchasing experience by offering localized payment options and currencies to meet the preferences of different markets. Consulting with localization specialists can help navigate these complexities.
Partnerships with Local Businesses
Collaborating with local businesses in target markets can enhance brand credibility and trust. Strategic partnerships, such as co-sponsoring events or supporting local charities, can facilitate market entry and foster community relationships.
Strategic Social Media Use
Leverage social media platforms strategically to engage with target audiences in different markets. Paid advertising, consistent posting, and collaboration with micro-influencers can amplify brand visibility and attract new customers. Adapting content and adhering to platform-specific norms and regulations are essential for effective social media branding overseas.
Implementing these international branding strategies can help businesses tap into new markets, increase brand awareness, and drive growth in emerging economies.
How International Brand Management is Done?
International brand management is essential for businesses seeking to establish a strong foothold in foreign territories. By implementing tailored strategies that resonate with local audiences while staying true to the brand’s identity, organizations can unlock new growth opportunities and establish themselves as global leaders in their respective industries.
For effective brand management, it is important to keep the following factors in mind.
- Consistent Brand Identity: Maintain a cohesive brand image across all markets to ensure recognition and trust among global consumers.
- Localized Marketing: Tailor marketing strategies to resonate with local cultures, preferences, and behaviors while staying true to the brand’s core values.
- Strategic Partnerships: Forge alliances with local businesses or influencers to enhance brand credibility and reach in foreign markets.
- Market Research: Continuously gather insights into international markets to understand consumer trends, competitors, and market dynamics.
- Effective Communication: Establish clear communication channels and guidelines to ensure consistent messaging and brand positioning worldwide.
- Adaptability: Remain flexible and adaptive to changing market conditions and consumer preferences in different regions.
- Brand Monitoring: Monitor brand performance, reputation, and customer feedback globally to identify areas for improvement and maintain brand integrity.
- Investment in Technology: Utilize technology and data analytics to optimize marketing efforts, track performance metrics, and enhance customer engagement on a global scale.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between departments, such as marketing, sales, and product development, to ensure alignment with international branding strategies.
- Continuous Evaluation and Improvement: Regularly assess the effectiveness of international brand management strategies and initiatives, and iterate based on insights and feedback for continuous improvement.
How to Build a Global Brand?
Building a global brand requires a meticulous blend of strategic planning, cultural sensitivity, and consistent messaging. It entails crafting a brand identity that resonates across diverse markets while remaining adaptable to local nuances and preferences.
From establishing a strong online presence to forging meaningful partnerships with local businesses, building a global brand involves a multifaceted approach aimed at fostering trust and recognition on a global scale.
By prioritizing brand consistency, authenticity, and customer-centricity, businesses can create a compelling narrative that transcends geographical boundaries and resonates with audiences worldwide.
Global Marketing and Branding
Global marketing and branding go hand in hand, serving as the cornerstone of a company’s international expansion efforts. It involves tailoring marketing strategies to suit the unique needs and preferences of diverse global markets while aligning with overarching brand objectives.
From conducting comprehensive market research to crafting localized campaigns and leveraging digital platforms, global marketing and branding encompass a spectrum of activities aimed at enhancing brand visibility, driving customer engagement, and ultimately, maximizing business growth on a global scale.
By embracing innovation, cultural understanding, and strategic agility, companies can effectively navigate the complexities of global markets and position themselves as industry leaders in an increasingly interconnected world.
What is Brand Consistency?
The brand consistency in global markets is crucial for maintaining brand identity internationally. It ensures that the brand message, design elements, and values remain uniform across diverse cultural landscapes.
By prioritizing global brand consistency, businesses strengthen their presence worldwide and reinforce brand recognition. Achieving consistency in international branding involves aligning marketing strategies with local preferences while staying true to the brand’s essence.
This requires implementing standardized brand guidelines, conducting regular audits, and fostering cross-functional collaboration. Emphasizing brand consistency as a cornerstone of the global strategy enables businesses to navigate international markets effectively, ensuring a cohesive brand experience that resonates with audiences globally.
Cross-cultural Branding Strategies
Cross cultural branding strategies involve tailoring marketing efforts to resonate with diverse cultural backgrounds. This approach acknowledges that what works in one culture may not necessarily work in another. To succeed, brands must embrace multicultural branding techniques and adapt their messaging, imagery, and values to different cultural contexts.
Key Strategies for Cross Cultural Branding
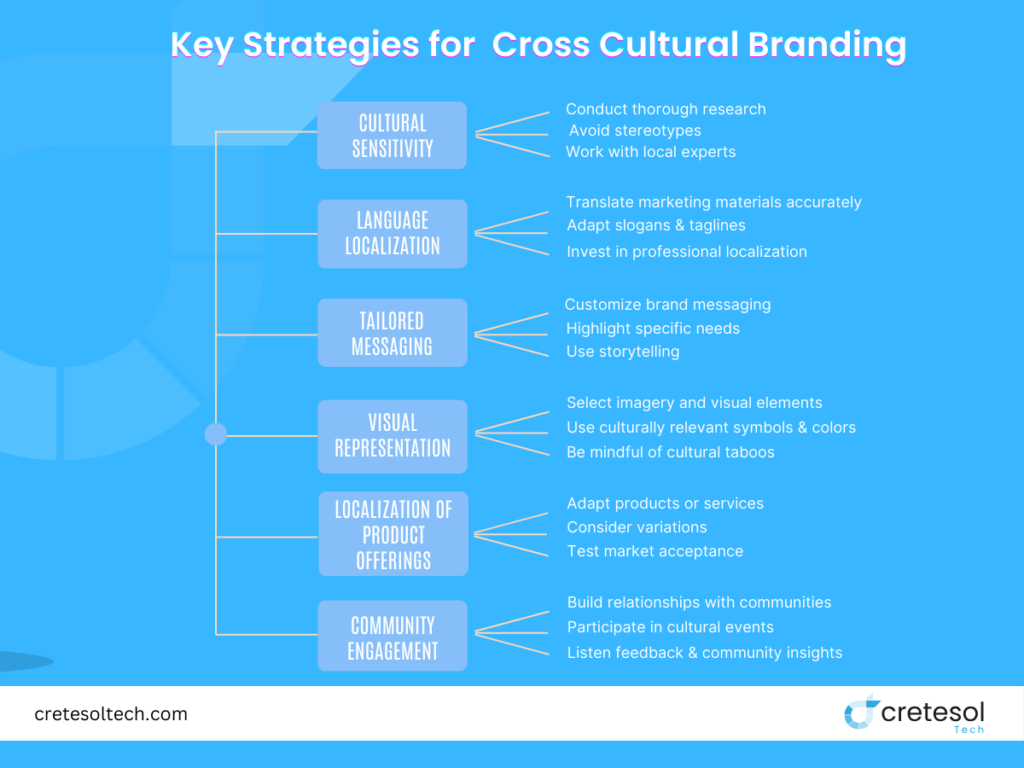
Cultural Sensitivity
- Conduct thorough research to understand the cultural values, beliefs, and norms of the target audience.
- Avoid stereotypes and clichés that may offend or misrepresent cultural groups.
- Work with local experts or consultants to ensure authenticity and cultural relevance in branding initiatives.
Language Localization
- Translate marketing materials accurately, considering linguistic nuances and idiomatic expressions.
- Adapt slogans, taglines, and product names to resonate with the linguistic preferences of the target market.
- Invest in professional localization services to maintain the integrity of the brand message.
Tailored Messaging
- Customize brand messaging to align with the cultural sensibilities and preferences of diverse audiences.
- Highlight how products or services address specific cultural needs or aspirations.
- Use storytelling to create emotional connections that transcend cultural barriers.
Visual Representation
- Select imagery and visual elements that reflect the diversity of the target market.
- Incorporate culturally relevant symbols, colors, and aesthetics into branding materials.
- Be mindful of cultural taboos or sensitivities when choosing visual content.
Localization of Product Offerings
- Adapt products or services to suit the preferences, tastes, and lifestyles of different cultural groups.
- Consider variations in packaging, sizing, flavors, or features to cater to diverse market needs.
- Test market acceptance through pilot programs or focus groups before full-scale implementation.
Community Engagement
- Build relationships with local communities through sponsorship, partnerships, or community initiatives.
- Participate in cultural events, festivals, and celebrations to demonstrate brand support and integration.
- Listen to feedback and incorporate community insights into branding strategies.
Effective cross-cultural branding strategies require a deep understanding of cultural nuances and a commitment to authenticity and respect. Businesses thrive by adapting marketing to diverse cultures, fostering connections, and sustainable growth in multicultural markets.
Case Studies on Global Branding
In the realm of global branding, few global branding case studies shine as brightly as those of Amazon and Samsung. These behemoths have not only conquered their domestic markets but have also cemented their positions as international icons of innovation and excellence. Let’s delve into their journeys to understand what sets them apart in the world of global branding.
Amazon
Today, Amazon holds the esteemed title of the most valuable brand globally, surpassing industry giants such as Google and Apple by being the first to surpass the US$ 200 billion mark in brand value. Hence, it’s impossible to discuss any other brand without acknowledging Amazon’s dominance.
Since its inception, Amazon has left an indelible mark. Founded by the visionary Jeff Bezos in 1994, during the nascent stages of the internet, what initially began as an online bookstore swiftly evolved into a colossal e-commerce entity in the United States.
Within its domestic sphere, Amazon solidified its brand identity, synonymous with value, convenience, and variety. Once establishing leadership in its home market, Amazon embarked on an assertive campaign to conquer international territories.
Across different markets, Amazon meticulously upholds its value proposition. Employing a keen focus on competitive pricing, swift deliveries, and an expansive product range, Amazon strives to claim the forefront in every market it ventures into.
Furthermore, Amazon’s scope transcends traditional retail, extending into realms like cloud services, artificial intelligence, digital streaming, and logistics. Consequently, the brand is intrinsically linked with technological innovation.
Amazon demonstrates a significant commitment to expansion by investing substantially in countries of interest. For instance, in Brazil, Amazon Web Services announced a staggering $1 billion investment in expanding cloud computing infrastructure in Sao Paulo. Similarly, in India, Amazon has erected over 60 distribution centers and 150 delivery stations to fortify its logistics network and enhance service capabilities.
With relentless investments in technology and infrastructure, Amazon steadily cements its position in various countries and industries, effectively outpacing local competitors. Thus, Amazon’s global branding narrative is underpinned by a staunch commitment to competitiveness.
Samsung
Samsung, the South Korean electronics titan, was established by Lee Byung-Chul in 1938. Initially, the company operated within the food processing and textiles sectors. It wasn’t until the late 1960s that Samsung made its foray into the electronics industry.
The global expedition of Samsung commenced in the 1990s, marked by the introduction of its mobile phones and televisions in international markets. Emphasizing innovation, quality, and design, Samsung’s offerings resonated with consumers worldwide. Additionally, the company’s strategy of catering to diverse market segments contributed significantly to its global triumph.
Samsung’s approach to international expansion revolves around comprehending and adapting to local contexts. By establishing research and development centers across various countries, Samsung endeavors to grasp local consumer preferences and needs. Presently, Samsung operates in more than 80 countries, underscoring that a locally rooted brand, coupled with a dedication to innovation and understanding of local markets, can attain global eminence.
The case studies of Amazon and Samsung offer valuable insights into the dynamics of successful global branding campaigns. Both companies exemplify the importance of staying true to core values while embracing innovation and adaptation. Whether it’s Amazon’s relentless focus on customer-centricity or Samsung’s commitment to understanding local markets, these brands serve as beacons of inspiration for aspiring global players. In an increasingly interconnected world, the journey of global branding is paved with challenges, but for those who dare to dream and innovate, the possibilities are limitless.
Final Thoughts
Navigating the complexities of global branding requires a strategic approach that balances brand consistency with cultural sensitivity. By understanding diverse markets, crafting compelling narratives, and fostering meaningful connections, businesses can build a strong global brand that resonates with audiences worldwide. This paves the way for sustainable growth and positions them as leaders in the international marketplace.
FAQS
What is a global brand and examples?
A global brand is a brand that is recognized and marketed worldwide, maintaining consistent identity, positioning, and marketing strategies across various countries and regions. Examples of global brands include.
- Coca-Cola: Known for its consistent taste and branding across the world.
- Apple: Offers the same products with uniform branding globally.
- Nike: Recognized for its athletic gear and “Just Do It” slogan worldwide.
- McDonald’s: Maintains its brand identity with localized menu items.
- Samsung: Known for its electronics and technology products globally.
What is the purpose of global branding?
The purpose of global branding is to create a strong, recognizable brand that transcends national borders. This includes,
- Building Brand Recognition: Ensuring that consumers recognize and trust the brand no matter where they are.
- Consistent Brand Message: Delivering a uniform brand message and experience across all markets.
- Economies of Scale: Reducing costs by standardizing marketing and production processes.
- Competitive Advantage: Establishing a robust market presence globally to outperform regional competitors.
What are the benefits of a global brand?
The benefits of a global brand include,
- Increased Brand Awareness: Enhances brand visibility and recognition worldwide.
- Market Share Growth: Access to a larger customer base across multiple countries.
- Customer Loyalty: Builds trust and loyalty through consistent brand experience.
- Cost Efficiency: Savings on marketing, production, and logistics through standardized operations.
- Greater Innovation: Leveraging global insights and resources to drive innovation.
- Enhanced Brand Equity: Stronger brand perception and value across diverse markets.
What are global branding strategies, and give examples?
Global branding strategies involve methods and approaches used by companies to establish and maintain a consistent brand presence internationally. Examples include,
- Standardization: Using a uniform marketing strategy and product offering worldwide. Example: Apple markets its iPhones similarly in all regions.
- Adaptation: Modifying products and marketing to suit local tastes and preferences. Example: McDonald’s offers localized menu items like the Maharaja Mac in India.
- Global Positioning: Establishing a unique brand position that appeals globally. Example: Nike promotes its brand with the universal slogan “Just Do It.”
- Glocalization: Combining global strategies with local adaptation. Example: Coca-Cola maintains its core brand identity while running localized marketing campaigns that resonate with local cultures.

 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates